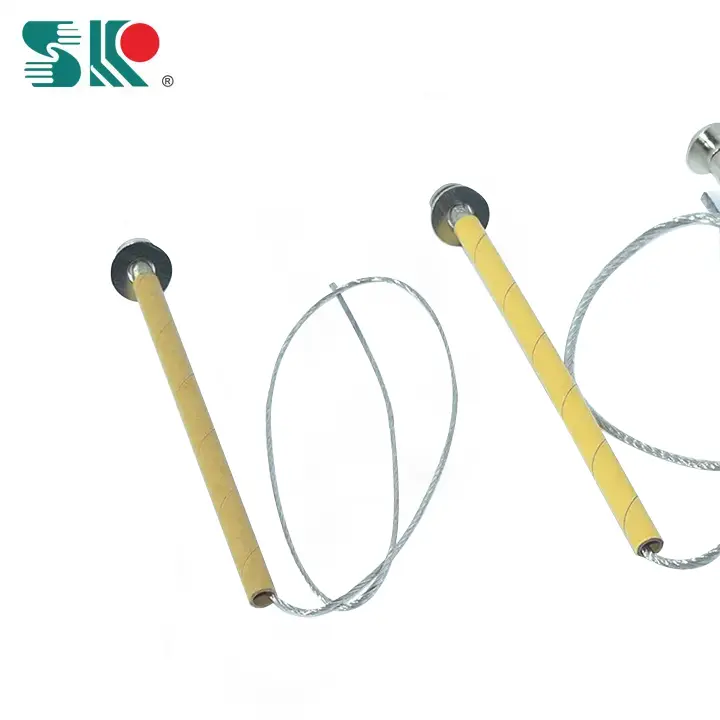
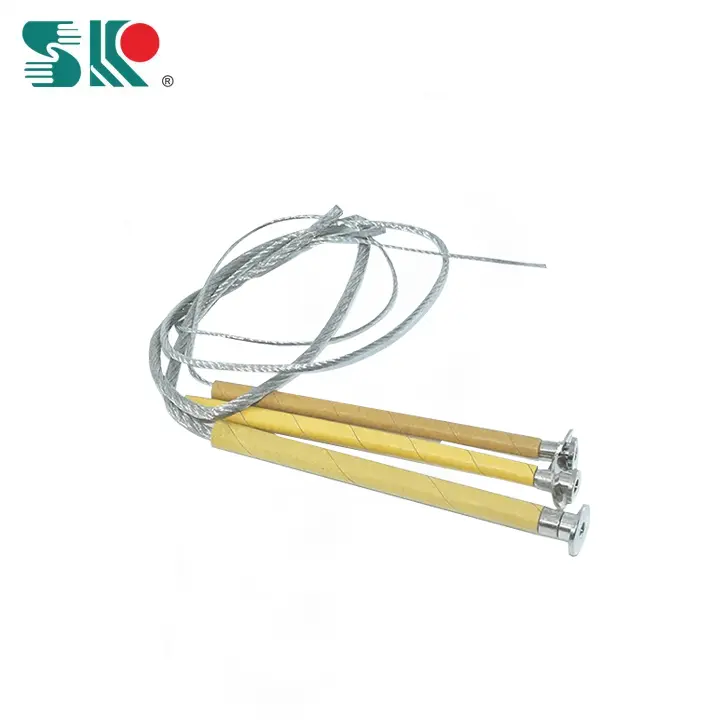
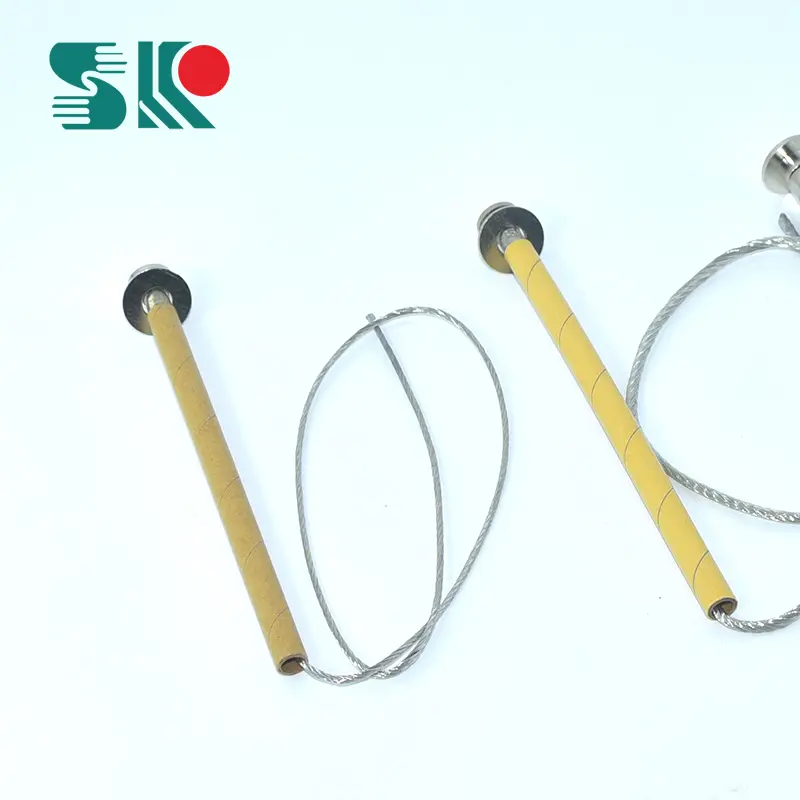
How to choose the correct fuse for drop-out fuses?
The fuse in the fuse and low-voltage load switch is connected in series in the circuit when working, and it plays an overload and short-circuit protection role for the line and electrical equipment. When replacing the fuse, what principles should be followed? Now it is described as follows:
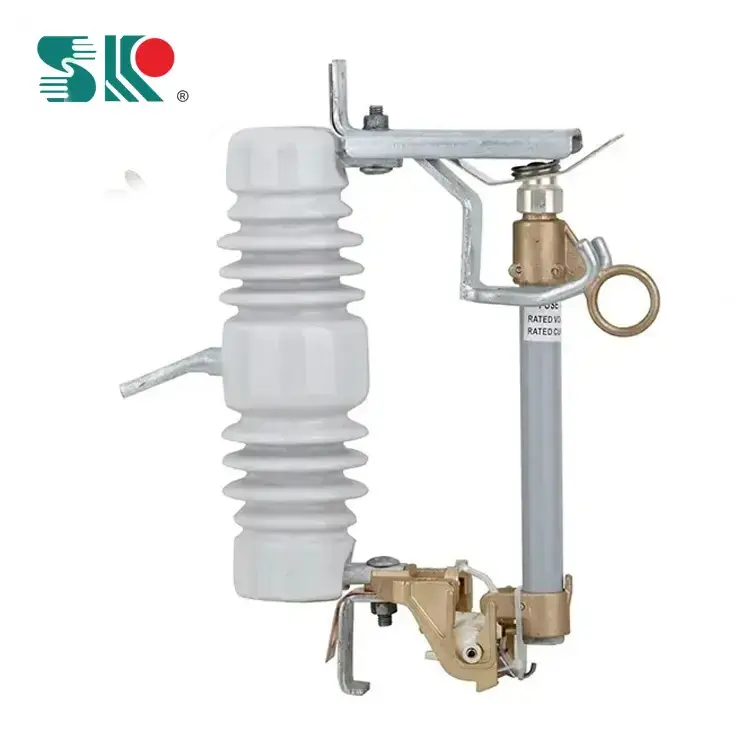
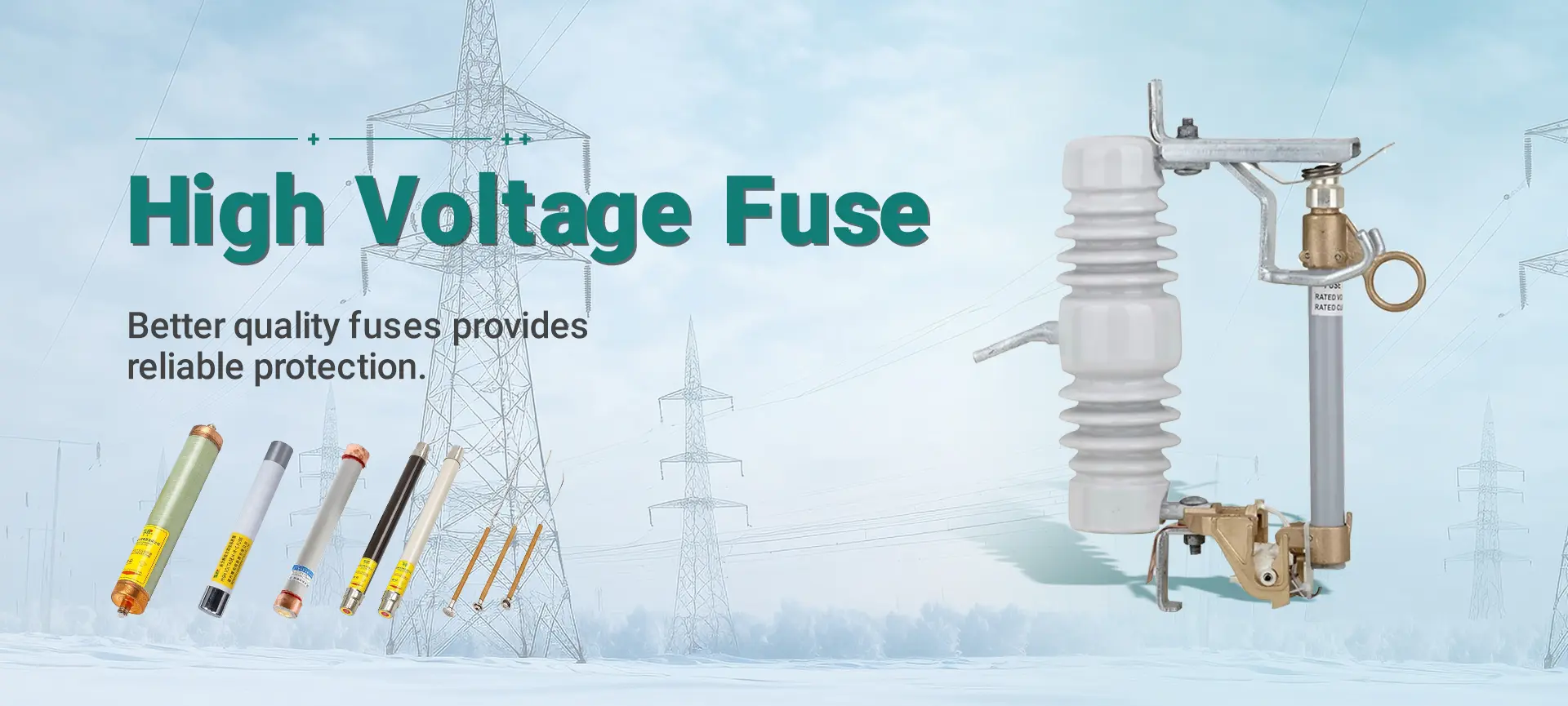
1. Copper and aluminum wires cannot be used as the internal fuse of high-voltage drop-out fuses.
The internal fuse of high-voltage drop-out fuses is generally made of materials such as copper and silver. Because copper and silver have very low resistivity and strong conductivity, the wire can be made thinner, which is conducive to arc extinguishing, but their melting points are very high, which can cause the fuse tube of the fuse to overheat and be easily damaged. Therefore, the melting point of the fuse made of silver and copper is artificially reduced by welding small tin beads or lead beads on the fuse. When the fuse is heated to the melting point of tin (232℃) or lead (327℃), the small ball melts first, causing the fuse to be interrupted. The arc formed at the interruption point causes the fuse to melt to both sides, thereby protecting the line or electrical equipment from being damaged by excessive current heating.
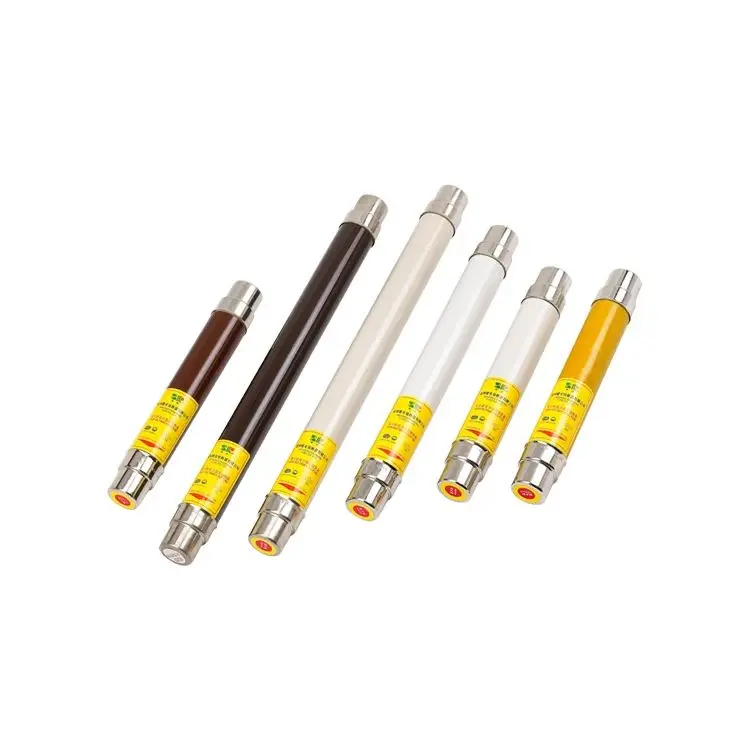
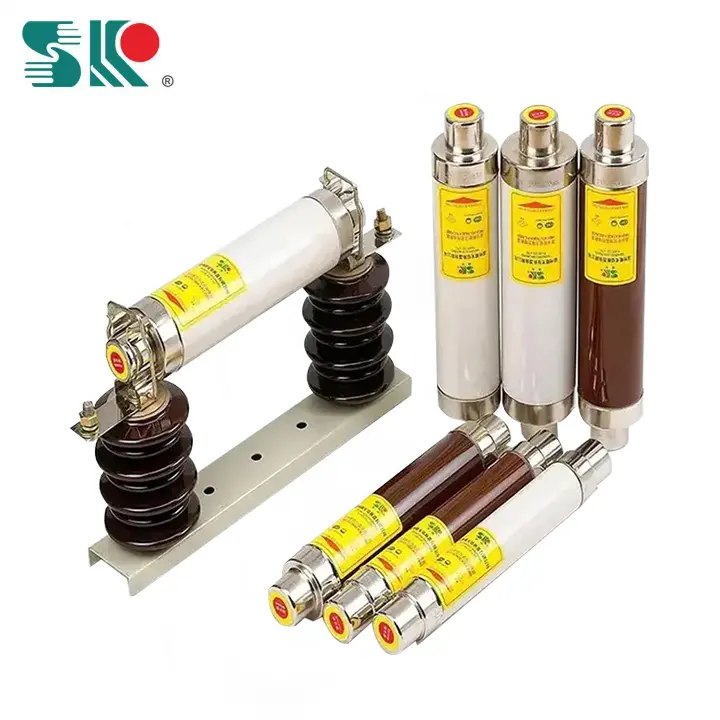
2. After the primary fuse of the 10kV voltage transformer is blown, it cannot be replaced by an ordinary fuse.
10kV voltage transformers are often protected by RN2 or RN4 type fuses. The rated current of the fuse is 0.5A, and the melting current within 1min is 0.6-1.8A. The fuse tubes of these two fuses are filled with quartz sand, so they have good arc extinguishing performance and large current breaking capacity (not less than 1000MVA). Because its fuse is made of nickel-chromium wire, the total resistance is about 90Ω, so it has the function of limiting short-circuit current. If it is replaced by an ordinary fuse, when the voltage transformer causes the fuse to melt due to a fault or other reasons, it can neither limit the short-circuit current nor extinguish the arc, which is likely to burn the equipment and even cause a system power outage. Therefore, when the fuse of the voltage transformer is blown, the original specification fuse should be replaced instead of an ordinary fuse.
3. High-voltage fuses filled with quartz sand can only be used in power grids with the same rated voltage.
For fuses filled with quartz sand, when the fuse melts, the arc burns in the narrow groove in the quartz sand. According to the arc extinguishing principle of the narrow gap, the arc is in close contact with the surrounding filler and is cooled and extinguished. It has a strong arc extinguishing ability and can extinguish the arc before the current reaches the peak value, which has a current limiting effect. However, it will generate overvoltage, and its overvoltage situation is related to the voltage at the place of use. If used in a power grid with a voltage lower than the rated voltage, the overvoltage may reach 3.5-4 times the phase voltage, which will cause the power grid to produce corona and even damage the equipment in the power grid. If used in a power grid with a voltage higher than its rated voltage, the overvoltage generated by the fuse may cause the arc to reignite and cannot be extinguished again, which will cause the fuse shell to burn out: while in a power grid with the same rated voltage, the overvoltage when fusing is only 2-2.5 times the phase voltage of the power grid, which is slightly higher than the line voltage of the equipment. So there is no danger.
4. When replacing the fuse (fuse), the rated current and rated voltage level of the fuse cannot be increased or decreased.
Only fuses with the same capacity and voltage level as the original ones can be replaced, otherwise the protection of the fuse will be lost.
5. The rated current of the fuse must be matched with the fuse.
Because the same type of fuse can be equipped with fuses with different rated currents, but the rated current of the fuse can only be smaller than the rated current of the fuse, at most equal, and never exceed. Because the rated current of the fuse is determined according to the heating conditions of the contact part and the terminal. For the same reason, the rated current of the load switch and fuse-type disconnector composed of the disconnector and the fuse must be smaller than the rated current of the switch, at most equal, and never exceed.
6. The rated current of the main switch and the sub-switch fuse must not be reversed or the same.
In general, the distribution lines are all controlled and protected by a combination of isolating switches and fuses. The rated currents of the fuses in the main switch and the sub-switch are different. The main switch has a larger fuse and the sub-switch has a smaller fuse.
7. Do not rashly replace the fuse of the load switch after it has blown.
Whether it is blown due to short-circuit current, overload current, or other reasons, do not rashly replace the fuse. Find out the cause and replace it after troubleshooting. At the same time, do not replace one phase after another, but replace all the fuses of the same load switch. Because the fuse that has not blown has also experienced heat, it is easy to blow in normal working days if it continues to be used. Therefore, the new and old fuses have some similar characteristics, but the fusing characteristics are different, and the cross-sectional area is also different.
8. The same load switch or fuse-type isolating switch.
The same type of fuse must be replaced. Do not mix and replace fuses of the same capacity but not the same type.
Because the fusing characteristics of different types of fuses are very different, for example, the fusing current of lead-tin alloy fuse is 1.5 times the rated current; while that of copper wire fuse is 2 times; and that of zinc fuse is about 1.3 to 2.1 times.
9. When replacing fuses, be sure to cut off the power supply.
Disconnect the isolating switch and never operate with power on to avoid electric shock accidents caused by the body or tools touching the live parts, and also avoid the possible accident of pulling out the fuse under load.
10. Do not let the fuse touch the shell.
When replacing lead-tin alloy fuses, when the length of the fuse is about 60 to 85 mm, the fuse must not be allowed to directly contact the protective shell during assembly.
When assembling copper wire fuses, the shell and the fuse must not be in direct contact, and the length must be sufficient. For wires with a diameter of less than 0.46 mm, it must be 60 to 85 mm long, and for those with a larger diameter, it must not be less than 100 mm. When replacing the fuse of small and medium-sized asynchronous motors, the rated current of the fuse cannot be 1.5 times the rated current of the protected motor, and should generally be about 2.5 times.
11. When replacing the fuse of a porcelain plug-in fuse, the asbestos padding inside the porcelain bottom cannot be removed or thrown away at will.
Fuses with a current rating of 30A or above are padded with asbestos padding in the arc extinguishing process for vibration reduction, heat insulation and arc extinguishing assistance.
12. The working mode of the spiral fuse cannot be changed at will.
Spiral fuses (RL1 type) have the advantages of strong current breaking capacity, small size, easy use, safety and reliability, and are widely used in the main circuit, control circuit and lighting circuit of electrical equipment for short-circuit protection.
When the fuse in its fuse tube is blown, a new fuse tube should be replaced according to the rated current of the load.
13. In the incandescent lighting circuit, fast fuses with small thermal capacity cannot be used as protection.
Because the instantaneous current of an incandescent lamp when ignited in a cold state is very large, it can reach 12 to 16 times the rated current of an incandescent lamp, and the duration of the starting impact current (the time to drop to the normal value) is 0.05 to 0.23 seconds (the greater the power of the bulb, the longer the time). The protection characteristics of the fast fuse: when breaking 4 to 6 times the rated current, the melting time is less than 0.2-0.02 seconds. This means that within the duration of the incandescent lamp starting impact current, the fuse of the fast fuse will melt.
14. Correct and reasonable selection of fuses is very important to ensure the safe operation of circuits and electrical equipment. The selection principles are: 1. When the current exceeds the normal value of the equipment for a certain period of time, the fuse should melt 2. When the electrical equipment is normally short-term overcurrent (such as motor starting, etc.), the fuse should not melt.
The selection method is (in environments without strict requirements other than the above):
1. Lighting and electric heating equipment circuits
(1) The rated current of the fuse in the main line is equal to 0.9-1 times the rated current of the watt-hour meter;
(2) The rated current of the fuse in the branch is equal to 1-1.1 times the sum of the rated currents of all loads in the branch.
2. AC motor circuits
(1) The rated current of the fuse in a single AC motor circuit is equal to 1.5-2.5 times the rated current of the motor;
(2) The rated current of the fuse in multiple AC motor circuits is equal to 1.5-2.5 times the rated current of the largest motor in the circuit, plus the sum of the rated currents of other motors.
3. AC welding machine
The fuse in the circuit of a single AC welding machine can be estimated by the following simple method:
(1) When the power supply voltage is 220V, the rated current of the fuse is equal to 6 times the power (kW) of the welding machine.
(2) When the power supply voltage is 380V, the rated current of the fuse is equal to 4 times the power (kW) of the welding machine.